
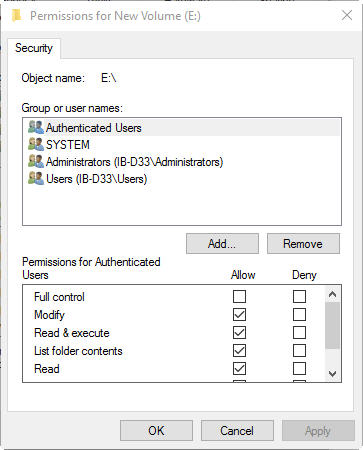
This lets you change the permissions to Read & Write for yourself while keeping the drive read-only for other users. If this is a drive you last formatted, you can change the individual permissions in the box above. The drive is encrypted, meaning you can’t access it in any way until you’ve decrypted the disk. The external hard drive uses a partially supported file system, like NTFS, which macOS only supports as read-only. The drive is set to read-only permissions, so you can’t add or delete files. This is partially because it can refer to a few different problems: The concept of unlocking an external hard drive on a Mac may not be familiar to you. What Does It Mean When a Hard Drive Is Locked on Your Mac? This isn’t often a major problem, and more often than not, it’s simple to solve. If you’re facing permission-related issues or can’t add files because the hard drive is locked, then the whole use of a hard drive is defeated. Whether you need to move a few files to another system or want to do a quick backup, it can never hurt to have a few of them around.īut an external hard drive is only convenient when you can use it. The use of an equal sign ( =) wipes all previous permissions for that category.No matter your operating system of choice, external hard drives can be useful in many situations. The u flag sets the permissions for the file owner, g refers to the user group, while o refers to all other users.
To remove all existing permissions, set read and write access for the user while allowing read access for all other users, type: chmod u=rw,g=r,o=r file.txt To set file permissions, you’ll use the chmodcommand at the terminal. RELATED: How macOS Catalina's New Security Features Work Setting File Permissions

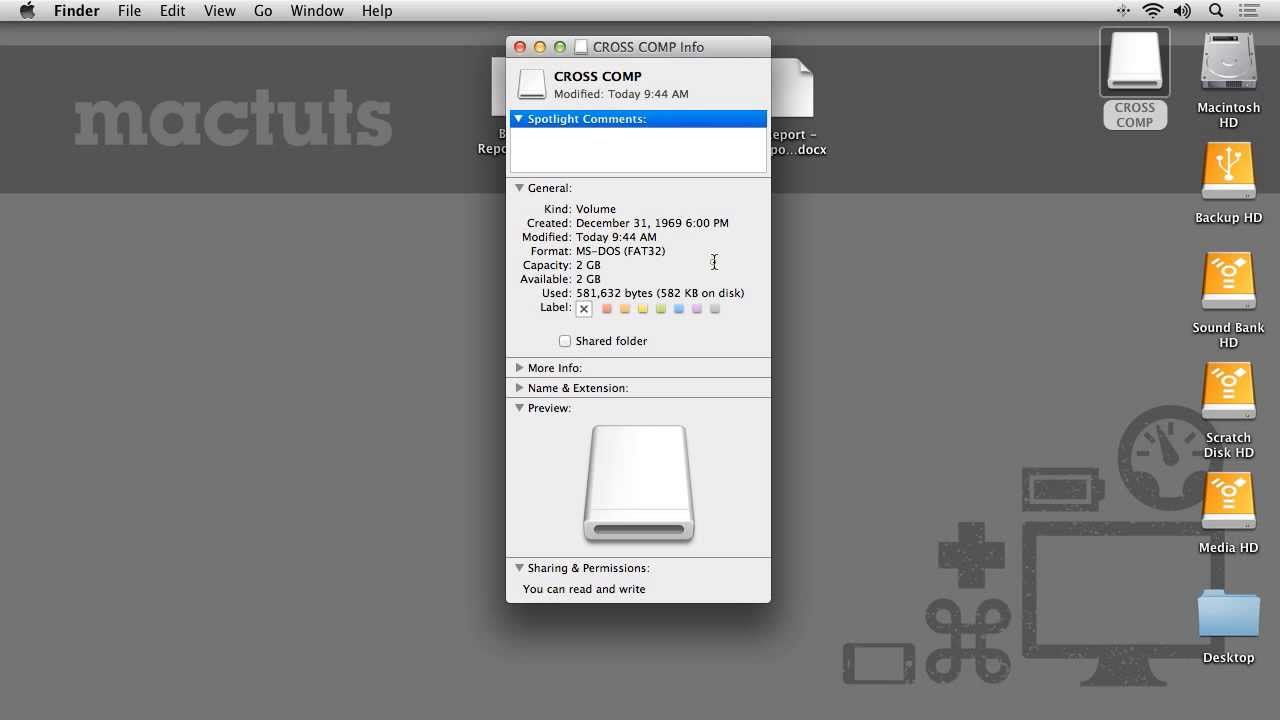
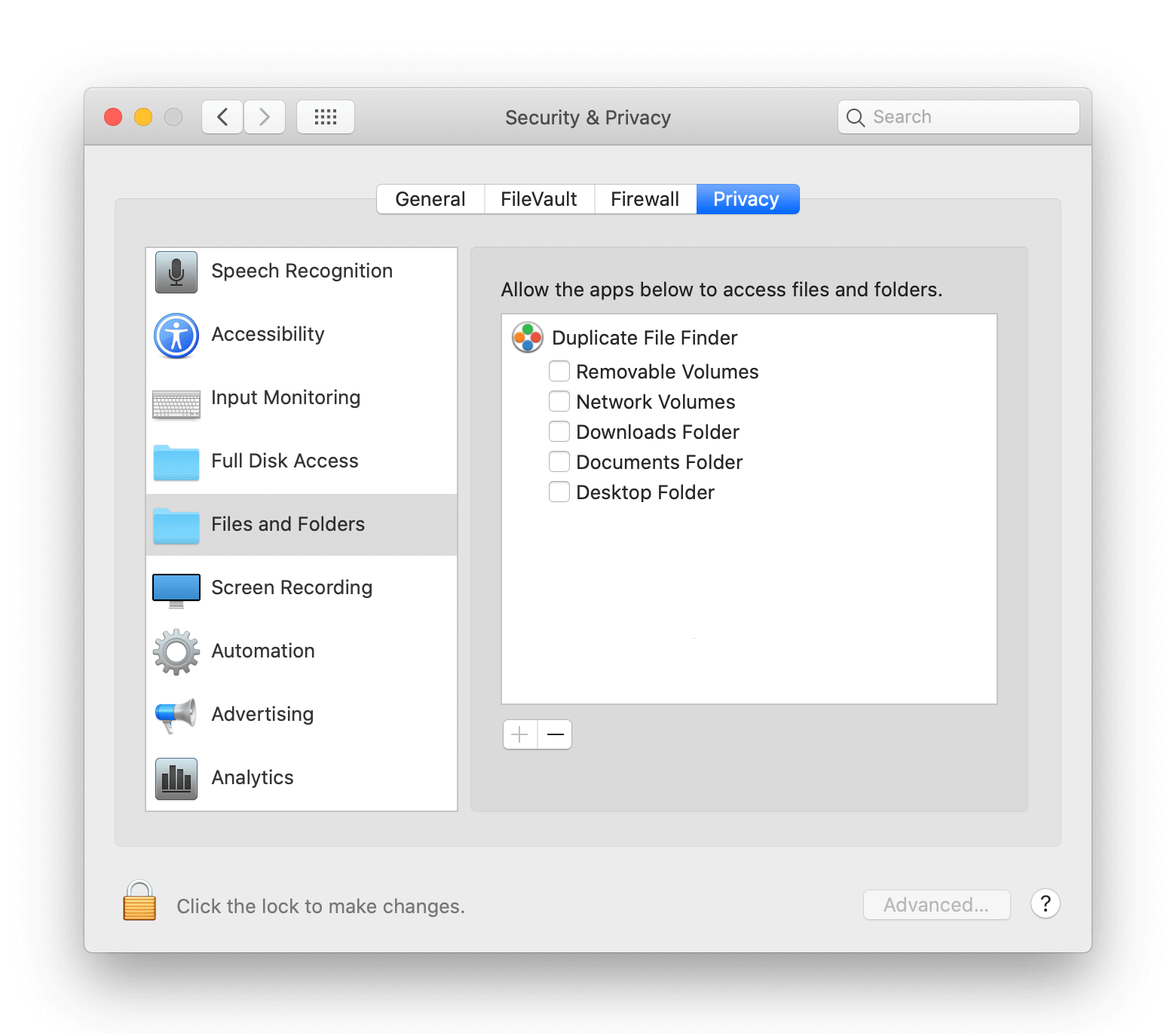
This is related in part to new security features introduced in macOS Catalina, although file access control lists (ACLs) have been a Mac feature since macOS X 10.4 Tiger back in 2005. If the final character is an at sign ( then it signifies that the file or folder has extended file attributes relating to security, giving certain apps (like Finder) persistent file access.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
